CDI International Report on US Trade Policies under the Trump Administration
Information

CDI International Report, themed on “US Trade Policies under the Trump Administration”, gathered experts and scholars to have an intense discussion on the current US trade policy and its possible influence on the Sino-US relationship.
Date: April 10, 2017
Venue: Room 101, CDI Mansion, Shenzhen
Host: CDI
Theme: US Trade Policies under the Trump Administration
Delegation from University of Amsterdam Visits CDI
 Students and teachers from University of Amsterdam visited CDI on March 31, and CDI experts on urban planning had academic exchange with them. The meeting is aimed at sharing Shenzhen’s successful experience in urbanization and construction of low-carbon city.
Students and teachers from University of Amsterdam visited CDI on March 31, and CDI experts on urban planning had academic exchange with them. The meeting is aimed at sharing Shenzhen’s successful experience in urbanization and construction of low-carbon city.
Urban villages in Shenzhen have been transformed successfully, so residents can live better and enjoy modern life. To construct low-carbon city, Shenzhen government not only made policies for saving energy, urban planning, space planning and feasibility studies, but also conduct energy-saving project for the government buildings, which contributed to the good environment for sustainability in Shenzhen. In addition, experts also provided guidance, analysis and advice for the graduate students on their case studies.
University of Amsterdam, one of the largest research universities in Europe with good reputation and high academic rankings, has produced several prime ministers of the Netherlands and Nobel laureates.
China's Economic Fluctuations and Structural Changes in 2017
Author: Fan Gang, President of CDI
Editor’s Note: The economic downturn in recent years are cyclical fluctuations which are resulted from overheated economy and investment. Besides, the functional and economic significance of the consolidation period of soft landing should not be underestimated. In addition, material consumption is far from over and investment should aim at new consumption models.
 The economic downturns in recent years are cyclical fluctuations.
The economic downturns in recent years are cyclical fluctuations.
Though China’s economy has been declining for six consecutive years, last year has witnessed some improvements. Deflation, indicated by the Producer Price Index, has basically come to an end in the second half of last year. The main problems now include overcapacity, inventory backlog and debts which are typical cyclical problems and the results of overheated economy and investment. To deal with these problems, we must cut excessive industrial capacity and conduct destocking and deleveraging.
The functional and economic significance of the consolidation period of soft landing shall not be underestimated.
There are different ways to deal with crises. Some market economies have opted for hard landing to address problems by rapid and massive restructuring, yet China is inclined towards soft landing as we do not want to lower the growth rate so much as to turn sporadic problems into systemic ones. The advantage of soft landing is that there will be neither negative growth nor recession while the disadvantage is that it is more time consuming.
It may take some time to address problems such as overcapacity, inventory backlog, debts and supply-side structural reforms. Regarding investment, consolidations, mergers and acquisitions are necessary for a variety of industries to improve concentration, which is in line with the law of the market, namely, survival of the fittest. In this way, China's economic and industrial structure will be further improved and thus lay the foundation for future growth.
Material consumption is far from over and investment shall aim at new consumption models.
China's economic structure is changing as consumption takes up an ever greater proportion. When income reaches a certain level, consumption will start to accelerate. The internet enables consumption to extend to small towns and rural areas.
Material needs are far from being satisfied in China and material consumption is still the primary concern for most Chinese people. Therefore, China's manufacturing industry shall never be ignored from investment’s point of view. Instead, it has great development potential with further adjustment, concentration and upgrading. At the same time, service consumption is indeed increasing and demand is expanding. Spiritual consumption ranging from movies and entertainment to fitness, pension and financial services is on the rise, which is also a major trend.
Nowadays there are debates around the world on the replacement of human employment by artificial intelligence. But if we take a deeper look, we would find that human beings have been trying to use machines instead of human labor to improve productivity, thus bringing about huge space for development of leisure and entertainment consumption.
Overall, in terms of investment, the odds of success will be higher if we pay more attention to using new technologies to meet the needs of the market and adjust the business model according to consumer demand so that supply and demand would be more balanced.
Treating Economic Sub-Health Conditions
Author: Fan Gang, President of CDI
Editor’s Note: at Session 24 Global Economy: Moving Beyond Sub-Health, Fan Gang said that high economic growth rate is unhealthy and China would like to lower its foreign reserves gradually.
 High economic growth is not necessarily healthy as China currently deals with the consequences of overheated economy in the past. China's central bank is also reluctant to hold $4 trillion in foreign reserves, hoping to lower it to the desired two trillion, yet the central bank does not want to see it happen overnight.
High economic growth is not necessarily healthy as China currently deals with the consequences of overheated economy in the past. China's central bank is also reluctant to hold $4 trillion in foreign reserves, hoping to lower it to the desired two trillion, yet the central bank does not want to see it happen overnight.
China's economic growth rate in 2007 was 14% and it returned to 12% after the crisis with the influence of stimulus policies. This kind of overheated growth is unhealthy. We are now actually dealing with the consequences of overheated economy. As long as the economy is stably growing without further recession, the current growth rate is fine.
Zombie businesses are already dead and need to be removed. Some debt-to-equity projects are still in progress and the closure of certain companies are also under discussion. These businesses are trying to find a way to solve the problem of layoff or unemployment, but no tangible results have been produced by now. Zombie businesses now still exist and are holding back the economy but the negative effect is not as serious as before.
Labor Market Reform in the Internet Era
Author: Fan Gang, President of CDI
Editor’s Note: at Session 28 Labor Market Reform: Tough, but a Must-Do during the Boao Forum for Asia Annual Conference 2017, Fan Gang said that freelancers who have emerged with the development of the Internet should be covered by social security system so that they could gain the social recognition and a sense of belonging to the society.
 With the development of the Internet, many non-traditional forms of employment have emerged, such as liberal profession, remote jobs, part-time employment, etc. However, in fact, these people may actually have pretty stable jobs, earning more than in large companies. Moreover, they can also enjoy more leisure time.
With the development of the Internet, many non-traditional forms of employment have emerged, such as liberal profession, remote jobs, part-time employment, etc. However, in fact, these people may actually have pretty stable jobs, earning more than in large companies. Moreover, they can also enjoy more leisure time.
Social security coverage should be made compulsory for these people so that they could enjoy the same benefits as others. Efforts shall also be made to make these forms of employment accepted by the general public.
Freelancers, in need of social recognition, may want to take part in social organizations and social institutions. We should give full play to the mechanisms of social associations in terms of social security and professional skills so that they can have a sense of belonging to the community. Training programs can be organized for freelancers to enable them to actively participate in social organizations, which will be important in the future.
Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Bay Area and China’s Opening-up
Author: Guo Wanda, Executive Vice President of CDI
Editor’s Note: Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Bay Area, a metropolitan area featured with vitality, technology and innovation, emphasized by Premier Li Keqiang in the Report on the Work of the Government 2017, implies greater opening-up of China.
 The world is now experiencing de-globalization. Yet China is stepping up opening-up to the outside world. Premier Li Keqiang proposed in the Report on the Work of the Government 2017 for the first time to work on the development planning of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Bay Area, which means that China now sets even greater store by opening up.
The world is now experiencing de-globalization. Yet China is stepping up opening-up to the outside world. Premier Li Keqiang proposed in the Report on the Work of the Government 2017 for the first time to work on the development planning of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Bay Area, which means that China now sets even greater store by opening up.
The Bay Area is a very important strategic hub for the One Belt and One Road. The guidelines proposed by the Belt & Road initiative, including policy coordination, facilities connectivity, unimpeded trade, financial integration and people-to-people bond will play a strong role in the Bay Area. In return, the Bay Area will inject new vitality into the Belt &Road initiative.
The Bay Area has considerable complexity. On the one hand, the legal systems of Hong Kong, Macao and the Chinese mainland are different; on the other, complexity also implies diversity and inclusiveness, which will make the Bay Area a place with huge potential for development as it is full of vitality and suitable for innovation.
Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Bay Area is a metropolitan cluster. First of all, the infrastructure connectivity shall be well planned. Only with facilitated commuting between different cities, can the flow of elements be efficient. Second, building a livable Bay Area is essential to attracting global talents. Other important considerations include financial opening and capital flow, etc. All of these require top-level design and solutions to overcome the existing institutional and legal barriers. Therefore, it is essential to establish a mechanism to solve these problems.
A dynamic and innovative bay area features a large number of immigrants, scientific and technological development as well as de-centering, with which Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Bay Area can be a match for San Francisco.
Growth Targets at Around 6.5%
 On March 5th, Prime Minister Keqiang Li announced in an address to Congress that China was aiming for growth of about 6.5% for 2017 and CPI of about 3%. He also mentioned the government would continue to implement a proactive fiscal policy and to maintain a prudent neutral monetary policy, in particular, M2 growth rate targeting at 12% y/y for 2017.
On March 5th, Prime Minister Keqiang Li announced in an address to Congress that China was aiming for growth of about 6.5% for 2017 and CPI of about 3%. He also mentioned the government would continue to implement a proactive fiscal policy and to maintain a prudent neutral monetary policy, in particular, M2 growth rate targeting at 12% y/y for 2017.
Price inflations slowed down in January-February. CPI experienced a large fall, dragged down by falling food prices, and rose 1.7% y/y, down 0.5 pps from last Q4. Ex-factory price index of industrial products rose 7.8% y/y, PPI rose 9.9% y/y, down 1 and 1.1 pps from last December, lowering for two consecutive months. We view the CPI decrease to be transitory but producer prices will continue to grow slower than before under tightening monetary policy.
In January-February, industrial output increased 6.3% y/y, up 0.2 pps from last Q4. Fixed asset investment excluding agriculture rose 8.9% y/y, up 1.1 pps from last Q4, largely from higher producer prices. Retail sales of consumer goods rose 9.5% y/y in nominal terms in January-February, down 0.9 pps from last quarter, and rose 8.1% y/y in real terms, down 1.1 pps and 1 pps respectively from last quarter. Imports in January-February rose 26.4% y/y, up starkly 23.7 pps from last Q4. Imports from developed countries also surged, possibly reflecting Chinese consumers’ higher quality demands. Exports were stabile as usual, growing at around 4% y/y.
In February, monetary policy continued its tightening. M1 rose 21.4% y/y, and grew around 20% y/y after canceling the Spring Festival effect, 1.4 pps lower than last December. M2 rose 11.1% y/y, down 0.2 pps from last December. Market interest rate increased. For example, the interbank deposits from AAA rated banks with maturity of one year had a return of 3.01% on November 1st, 2016, but rose to 4.18% in this March, up more 1 pps. The heightened market interest rate has negative effects on corporate financing. Net financing from corporate bond grew negatively for three consecutive months.
According to National Bureau of Statistics, real estate prices in China’s major cities rose around 50% y/y in the year of 2016. Property sales by area still rose 25.1% y/y in January-February. Local governments are now taking further steps to stabilize housing market by strengthening their cities’ housing purchase restrictions. We view there might be some corrections in China’s “first tier” large cities such as Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen, but prices in second tier cities, mostly key provincial capitals, may remain to be sable, while small cities and towns in vast countryside (not those towns nearby large metropolitan areas) may continue to fall slightly in 2017. Our judgment is based on China’s sound GDP growth rate and top tier cities’ superior public goods provisions.
The Global Financial Centres Index 21 (GFCI 21)
 Click here to download the full report as PDF.
Click here to download the full report as PDF.
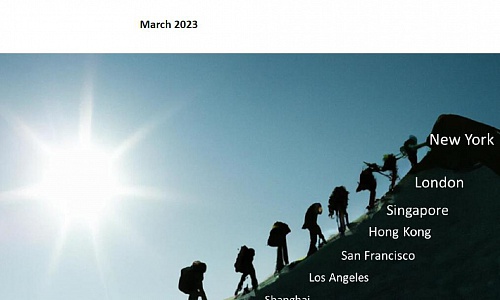
London, New York, Singapore, Hong Kong and Tokyo remain the five leading global financial centres. However, Brexit and the US election have had a significant impact. London and New York fell 13 and 14 points respectively. These are the largest declines (except for Calgary) in the top 50 financial centres. Singapore rose by eight points and is now only 20 points behind New York.
There are six cities of mainland China rated in the GFCI 21, including Shanghai, Beijing, Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Qingdao and Dalian. Shanghai got 715 points, ranks 13rd, rising 3 places in the rankings. Beijing rose significantly, rising ten places. Both Shanghai and Beijing are in the top 20 financial centres. Shenzhen got 701 points, ranks 22nd. Guangzhou has been enlisted in GFCI Index for the first time and did well with 650 points, ranks 37th. Qingdao won 640 points and ranks 8th just behind Guangzhou. Dalian fell to 75th in the rankings. Apart from that, Chengdu and Hangzhou are regarded as associate financial centres.
GFCI 21 was launched simultaneously in Milan and Shenzhen by the Z/Yen Group and CDI which marked the second collaboration between CDI and the Z/Yen on the compiling of GFCI.
The Global Financial Centres Index 21 Launch
Information
 The Global Financial Centres Index 21 (GFCI 21) was launched simultaneously in Shenzhen, China and Milan, Italy on March 27th, 2017. GFCI 21 was jointly compiled by the Z/Yen group and CDI. Key financial centres were scored and ranked from the perspectives of business environment, financial system, infrastructure, human capital, and reputation. CFCI 21 launched the latest scores and ranks of 88 financial centres and analyzed the situations, features and trends of development.
The Global Financial Centres Index 21 (GFCI 21) was launched simultaneously in Shenzhen, China and Milan, Italy on March 27th, 2017. GFCI 21 was jointly compiled by the Z/Yen group and CDI. Key financial centres were scored and ranked from the perspectives of business environment, financial system, infrastructure, human capital, and reputation. CFCI 21 launched the latest scores and ranks of 88 financial centres and analyzed the situations, features and trends of development.
Date: March 27, 2017
Venue: Room 101, CDI Mansion, Shenzhen
Host: CDI, Z/Yen Group
Theme: The Global Financial Centres Index 21
CDI Holds OBOR Roundtables in Italy and Greece
 OBOR Roundtables were held jointly by CDI and The European House-Ambrosetti and The Hellenic Foundation for European & Foreign Policy in Italy and Greece respectively. During the visits in three cities including Milan and Rome in Italy and Athens in Greece from December 4 to 11, 2016, CDI also had roundtable discussions with The Italy-China Foundation, Borsa Italiana, The Italian Banking Association, Athens Exchange Group and Eurobank Ergasias.
OBOR Roundtables were held jointly by CDI and The European House-Ambrosetti and The Hellenic Foundation for European & Foreign Policy in Italy and Greece respectively. During the visits in three cities including Milan and Rome in Italy and Athens in Greece from December 4 to 11, 2016, CDI also had roundtable discussions with The Italy-China Foundation, Borsa Italiana, The Italian Banking Association, Athens Exchange Group and Eurobank Ergasias.
In the discussion on the OBOR with Ambrosetti in Milan on December 5, CDI delegation elaborated on China's opening-up strategy, China's investment in the EU, China's economy, the RMB exchange rate, Shenzhen-Hong Kong Stock Connect, the opening-up of China's capital market and other issues. More than 30 representatives from Italian think tanks and businesses raised questions about the Silk Road Fund and logistic connectivity along the Belt and Road. They showed interest in participating in the OBOR, but they hoped to know more about the Chinese demands, participation channels and cooperation approaches. Therefore, it is imperative for the two parties to enhance the communications on the OBOR.
CDI delegation also met with more than 20 think tank experts, business managers and government officials in the roundtable discussion with The H-ellenic Foundation for European & Foreign Policy in Athens on December 9. It is noted that many Chinese enterprises, such as Huawei, ZTE and Fosun, are now expanding their business network in Greece. For example, China COSCO Shipping Group has acquired 51% of Piraeus Port. It is agreed that Greece has the historically honored ports and and shipbuilding industry which are attractive to foreign investment. In addition, Greece is willing to leverage the OBOR investment opportunities.
During the visits to other institutes, it is also found that experts and business managers from Italy and Greece also paid close attention to the opening-up of China's capital market such as Shanghai-Hong Kong Stock Connect, Shenzhen-Hong Kong Stock Connect.
The activities expanded investment opportunities in the countries along the Belt and Road. Italy has expressed interest in OBOR projects concerning finance and logistics, while Greece is looking forward to introducing Chinese capital to airport, hot spring, telecommunications, retailing, etc. Hence, Chinese enterprises can tap more investment opportunities in the European market.
https://en.cdi.org.cn/component/k2/itemlist/user/352-superuser?start=440#sigProId3a75be9134