2018 - Insights

Author: Fan Gang, President of CDI
Editor’s Note: China’s central government has made important adjustments to the urbanization strategy, shifting from the strategy to develop small towns to developing large cities. Crucial to building big cities and large city clusters is the integration of transport and public services.
In the past 40 years of reform and opening up, China has experienced the largest and fastest industrialization and urbanization process in world history. At present, only about 55% of Chinese live in cities, and the process of urbanization is far from over. Recently, during the China International Import Expo, President Xi Jinping proposed to support the regional integrative development of the Yangtze River Delta as a national strategy. Recently, the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the State Council issued the “Opinions on Establishing a New Mechanism for More Effective Regional Coordination and Development”, which mandated the integrative development of major regions driven by the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei cluster, Yangtze River Delta cluster, Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area and Chengdu-Chongqing cluster. These recent developments signal a strategic shift from encouraging the development of small towns to that of big cities and large city clusters.
China will form a “3+N” city cluster layout.
The polarization of China’s real estate market is in essence a result of increasingly polarized population flow, which will lead to the formation of three super city clusters with a population of 100-200 million, and a number of big city clusters with a population of 30-50 million. The Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, the Yangtze River Delta, and the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao region have the potential for becoming super city clusters, while Wuhan, Zhengzhou, and the Chengdu-Chongqing region will likely see the emergence of big city clusters.
The development of big cities and large city clusters, in itself a response to people’s pursuit of a better life, conforms to the current dynamics of population movement and will contribute to economy of scale and the agglomeration effect. In this process, it is crucial to have a broad vision, for it would be necessary to draw lessons from the development of other countries and proactively make city plans in line with urbanization trends. The first priority is effective transport system that enables people to work and live in separate zones or cities, thus making it possible for big cities and surrounding small towns to have different functions. This also requires that small cities and towns around big cities have different functions to avoid overlaps.
Promoting regional coordination by drawing on China’s historical experience of “Imperial Commissioners” and “Provincial Governors”
To further promote the construction of large city clusters, it is imperative to solve problems of current administrative divisions for effective overall planning so that economic, industrial and research sectors within the region can complement each other in a coordinated way.
Large-scale regional planning is often hindered by administrative divisions, which requires coordination and guidance at a higher level. Compared with the joint deliberative organs such as the council of New York bay among other bay areas, effective coordination mechanisms in many domestic city clusters are yet to be formed. Measures such as holding annual joint meeting among city mayors so that they can share views on their own cities’ development and explore possible solutions for integrative growth are by no means easy to achieve.
In this respect, we can draw lessons from China’s historical experience: all dynasties in China have official positions such as the “Imperial Commissioner”, “Governor of Two Provinces”, “Governor of Guangdong and Guangxi”, etc., which are responsible for coordinating work in a case-by-case approach.
By far several regional coordination mechanisms have formed in China. The State Council has set up a Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Collaborative Development Leading Group headed by China’s Vice Premier. The Yangtze River Delta and the Pearl River Delta may also require such an arrangement. Within a cluster, cities shall avoid forming similar industrial structure, but instead, develop a range of industries in different areas as well as different small city layouts to ensure coordination and complementarity.
Public services shall be enhanced for city clusters.
Strengthening the integration of public services is also crucial, including ensuring cross-regional coordination of medical services and equal access to education. It is important to minimize the influence of the household registration system and strive to achieve equal access to public services for permanent residents. This process will entail reform in economy, society and governance and will require the efforts of think tanks, research institutions and associations to jointly facilitate the sound development of urbanization.

Author: Fan Gang, President of CDI
Editor’s Note: It is imperative to reexamine fundamental aspects as we innovate the financial sector in order to ensure a bright prospect for its future development and to actually solve current problems.
The further development of China’s financial sector is unstoppable and is also something determined by China’s economic trends. Still, problems such as high leverage, risks and debts remain, which needs further investigation and analysis. Banks are constantly upgrading the technologies they use, such as APPs, networks, the internet, Fintech and big data, which are only natural as new technologies should be embraced by all industries. But the reason why the above-mentioned problems persist or are even worsening, especially regarding debts and the stock market, even as we try to innovate the financial sector, in my opinion is due to weak fundamentals. These fundamentals should be reexamined in the innovation process. As a late-mover, China wants to catch up with and even overtake advanced countries, but tends to only focus on the attractive side of finance but ignore its underlying rationale and past lessons of development. Thus it is important to consider how the financial sector should be developed by revisiting the fundamentals; this is the only way to effectively address the current problems to ensure robust prospect for the financial sector in future.
- Common sense
Money can be generated through investment but can never come out of thin air. The Ponzi scheme and any other financial practices that promise sustained high returns on investment are all frauds. Another common sense is about financial market regulation, especially for public finance. Regulation encourages innovation, provides confidence that risks can be controlled, and thus facilitates the development of new technologies and sound development in general.
- Fundamental integrity
Fundamental integrity refers to basic systems including legislation that punish and take preventive measures against dishonest behaviors. The essence of finance is credit, without which its development will go awry.
Mergers and acquisitions are a notable example. One main mission of finance is to ensure the survival of the fitter enterprises in the economic cycle, as less competitive enterprises are acquired by more competitive ones, so that their productivity can be more effectively used. But endless back-door deals following mergers and acquisitions render projects not operable. It is necessary to establish a credit system, otherwise the market will always face insurmountable challenges. Take for instance block chain, which is designed to make information transmission smoother and ensure privacy, therefore a means to reduce cost of enterprises and individuals in economic terms, including cost to expose false information or overcome information asymmetry. But the essence of block chain is providing information. If it contains false information, or in other words, if fundamental integrity is undermined, then information technology will only bring us disaster rather than progress. This means we should first address the basic issue of integrity.
- Fundamental nature
Finance, which provides money to users by acting as an intermediary based on credit, is in nature a service industry that accommodates the needs of the real economy. Through banks, securities, funds, insurances and financial management, the financial sector channels capital into the real economy to fuel its growth. Starting from investing in funds to developing the capital market is one way to develop the real economy.
4 Fundamental business forms
One important cause for lack of innovation in investment funds is not with finance, but with the property rights system. This goes back to the basic institutional issues, again that of property rights, not finance.
First, personal intellectual property rights can be capitalized and turned into stock rights to attract venture capital and concentrate capital and resources in the fields of scientific and technological innovation. The absence of corresponding systems has resulted in limited investment in new enterprises. Enterprises think that financing is to borrow money from banks, which is both costly and difficult. If funds are robust, enterprises would naturally be invested in by funds. Banks only provide liquidity for enterprises, while investment funds underpin their long-term development.
Secondly, many basic business forms have not been developed, such as financial intermediaries for mergers, acquisitions and reorganizations. This is also one fundamental issue that should be reexamined.
- Fundamental systems
The innovation of the financial sector and its further development depend on a robust fundamental system. Once they find advanced technologies, less developed countries tend to mistakenly focus only those latest technologies while ignoring the systems behind.
It is important to cement fundamental aspects as we embrace new technologies. As a result of the lack of a well-functioning fundamental system, coupled with the absence of fundamental common sense and corresponding means of regulation, new problems and frauds will emerge following the use of new technologies. This does not mean that innovation is bad, but that great importance shall be given to fundamentals in the process of innovation. Only in this way can the whole financial sector develop in a more sound and balanced way to better contribute to China’s economic development, the generation of wealth, and more efficient operations of capital and investment.
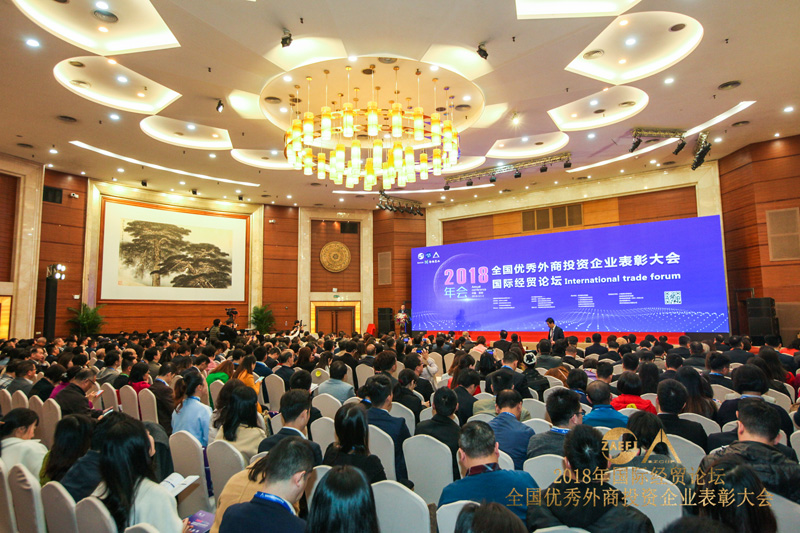 On December 11, the 2018 International Trade Forum was held in Shenzhen by China Development Institute in collaboration with Shenzhen Association of Enterprises with Foreign Investment among other institutions, where economists, entrepreneurs and government representatives held discussions on the international economic landscape, as well as opportunities and challenges for businesses amidst rising global trade tensions.
On December 11, the 2018 International Trade Forum was held in Shenzhen by China Development Institute in collaboration with Shenzhen Association of Enterprises with Foreign Investment among other institutions, where economists, entrepreneurs and government representatives held discussions on the international economic landscape, as well as opportunities and challenges for businesses amidst rising global trade tensions.
“It is important for China to find new growth momentum in reform.”
Recent years have witnessed the rise of “de-globalization”. It is thus imperative for China to develop a new economic growth model driven by increased productivity. Regarding the supply side, China shall prioritize the supply and allocation of labor, and reform its education and professional training sector in order to facilitate growth of higher quality in future. Regarding the demand side, China shall improve income distribution system and foster higher consumption capacity of its people to further fuel economic growth. In addition, China shall also ensure basic public services as well as equal access to these services.
—— Cai Fang, Member of the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress, Vice-President of the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences and Chairman of the Board of Directors of the National Institute for Global Strategy.
“The mobility of production factors is the key to building a global technology innovation center for the Greater Bay Area.”
Currently, the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area faces 5 major challenges in the movement of people, i.e., difficulty for professional accreditation and restricted scope of practice, higher individual income tax in China’s mainland compared to that in Hong Kong and Macao, non-portable social security, difficulty in actualizing equal treatment, and lack of supporting facilities. To address these challenges, the institutional arrangements for the movement of people in the Greater Bay Area shall be innovated, such as unilaterally recognizing the professional qualification of Hong Kong and Macao residents, extending the practice of “separate tax schemes for Hong Kong and Macao people” across the Greater Bay Area, exploring effective ways to link the social security systems of Hong Kong, Macao and the mainland, building Hong Kong and Macao Residents Services Center in the Greater Bay Area, piloting equal treatment for Hong Kong and Macao residents in the Greater Bay Area and fully capitalizing on big data to facilitate the movement of people.
—— Guo Wanda, Executive Vice President of China Development Institute.
The important role of multinationals in economic globalization.
To gain an upper hand in global competition, multinationals shall firstly establish global presence to ensure sustained supply and to establish communication with global clients, and secondly, engage in innovative cooperation in diverse dimensions, and provide more effective solutions for clients, and thirdly, ensure good service and quality commitment to win brand recognition, and fourthly, provide diverse products and one-stop services.
—— Huang Yiyun, General Manager of Dupont China Holding Co., Ltd
“Two-way” asset management competence will be a key advantage in international asset management arena in future.
For a long time in the past, China’s investment in overseas assets has been lacking, and vice versa. This imbalance will be overcome with increased mobility of China’s capital market. Domestic and overseas institutions shall explore different avenues of asset management in search of new systemic hedging strategies to improve resilience in investment and reduce fluctuations.
—— Sun Chen, Chief Executive of Harvest Global Investments Limited
Shenzhen shall seize the opportunity of the development of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area and make China’s voice heard in international rules.
Under the Belt and Road Initiative, China’s foreign trade and overseas investment have maintained steady growth. China shall stand up to the new problems that have emerged in international arbitration through legislation or judicial interpretation with even more open mindset. On this front, Shenzhen is dedicated to fostering business environment in sync with international rules, such as internationalizing the governance structure, organization and scope of practice of Shenzhen’s arbitration institution, in a bid to create a new pillar for international arbitration.
—— Liu Xiaochun, President of Shenzhen Court of International Arbitration and Director of Shenzhen Arbitration Commission
Shenzhen’s enterprises shall improve their ability to work with international rules
An increasing number of enterprises in Shenzhen have gone global under the Belt and Road Initiative. These enterprises urgently need to familiarize themselves with local legal system, financial environment and cultural customs. Thus it is important to continue to educate enterprises to ensure their compliance with and respect for international rules, as well as their ability to protect their own legitimate rights using these rules.
—— Gao Zhan, Member of the CPPCC Shenzhen Committee, head of Shenzhen Fair Trade Promotion Administration
European enterprises maintain confidence in investing in China as business environment improves in the latter.
In 2017, European businesses have achieved robust financial performance in China, with 66% of respondent businesses reporting year-on-year revenue increase. Meanwhile, the steady improvement of China’s business environment has boosted European investors’ confidence in operating in China. As to the rising challenges posed by increased production cost, Chinese and German businesses shall deepen high-tech talent training cooperation, so as to provide technical support to cope with labor shortage and faster pace of industrialization.
—— Sven-olaf Steinke, General Manager of TüV Rheinland’s electrical service in China
Businesses shall proactively conduct upgrading to cope with the negative impacts of trade frictions.
As China-US trade frictions continue to ferment, global business operations and investment will face uncertainties. Enterprises shall keep a level head and increase R&D investment in big data and other advanced technologies to boost industrial upgrading, reduce cost and improve efficiency, so as to avert the risks posed by trade frictions.
—— Kang Yong, Chief Economist at KPMG China
The Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area has huge potential, and business complementarity and cooperation shall be encouraged.
The economy in the Greater Bay Area has great potential for growth. Different cities and businesses within the Greater Bay Area shall seek effective cooperation based on mutual complementarity. The Federation of Hong Kong Industries will help its member enterprises in their upgrading process, develop new innovative technology platforms, provide businesses with consulting services and match-making opportunities, and facilitate cooperation between experienced industrialists and start-ups.
—— Sun Qilie, Honoary President of Federation of Hong Kong Industries
https://en.cdi.org.cn/component/k2/itemlist/category/83-2018-insights?start=0#sigProId48c63f73b5
 Author: Fan Gang, President of CDI
Author: Fan Gang, President of CDI
Editor’s Note: After acquiring the shares of private enterprises, large state-owned capital tends to operate private enterprises with SOE management mechanisms. This practice undermines economic flexibility.
In recent years, state-owned enterprises have become less energetic. New regulations set up in the national anti-corruption campaign have put SOEs under more rigorous supervision, resulting in slower decision-making process and less capacity for risks. Thus the government shall consider how to further develop the private economy. The next round of economic growth needs to be underpinned by independent innovation, which inevitably comes with huge risks. Compared to SOEs, the private sector is energetic and more willing to take risks. A risk-taking spirit coupled with a good decision-making mechanism is prerequisites for fully realizing independent innovation and market flexibility to inject vigor into economic development.
Despite a lot of support given by the central government in legislation and policies to the private sector to protect their interest and create a more enabling business environment, the operation mechanisms of private enterprises are often incorporated into SOE management after their shares are acquired by state-owned capital. Although capital has remained unchanged in the short term, this practice represents an unfavorable trend in the long run as it undermines economic flexibility. To better utilize state-owned capital to serve the private sector, the preferred stocks are desirable as they allows SOEs to invest in private enterprises for profit without imposing their own management system on the latter. In this way, private enterprises can maintain their vigor while assuming risks by themselves.
 Author: Fan Gang, President of CDI
Author: Fan Gang, President of CDI
Editor’s note: In terms of the recent Sino-US trade friction, Prof. Fan Gang thinks that it can be solved, only not with a single agreement, but step by step with multiple negotiations. In the long run, China should strengthen incentive mechanism for technology innovation to better foster independent innovation.
- On the current economic situation
Over the past 40 years, China’s economy has seen fluctuating high growth, while still in the process of adjustment. There are two views about the current economic situation. Optimists think that a new cycle is coming, while pessimists think that deleveraging and regulation will lead to tight liquidity. I’m not that optimistic, I don’t think that China’s economy is entering a new cycle now, and a lot of problems remain unresolved, including deleveraging and de-capacity. The resent reduction in reserve ratio released liquidity and restored it to its proper level, which is a neutral policy, and should not be interpreted as expansionary or tightening policy. In this sense, I am also not that pessimistic.
- On China’s long-term economic development and Sino-U.S. trade friction
United States trade deficit cannot be solved due to two reasons. First, U.S. savings rate is low. Second, as an international currency, other countries need to purchase goods from the U.S. in exchange for dollars, at the same time do not sell goods to U.S. or spend U.S. dollars, thus creating trade deficit. Among these countries, U.S. has the most extensive deficit problem with China due to the huge trade imbalance. In the trade of productions, China’s strengths are low and middle end manufactured goods, while Unite States are more advanced in high-tech and arms trade. As economy is booming in China, there are more products to be sold. Meanwhile, export control is tightening in United States, giving China less purchase options. As a result, trade imbalance increases. The United States penalized ZTE, at the same time restricted the export of high-tech products, exacerbating trade deficit. Although the two countries are hoping to reach on an agreement, it is always possible that U.S. will exit the agreement as they have done so multiple times recently. Therefore, Sino-U.S. trade fiction cannot be settled through single negotiation or agreement, but in multiple steps and stages.
On the other hand, it is apparent that U.S. is focusing on restricting China’s technology advancement. However, China’s technology and economic development is definite, therefore making the problem irreconcilable. China’s first stage of economic growth depended on cheap labor, i.e. comparative advantage. The second stage of growth depended on relative advantage or late-mover advantage, in other words learning from knowledge and technology spillover of other countries. Establishment of joint ventures is a perfect example. Unites States has noticed this trend and may disconnect the learning process. In the future, our researchers may be restricted from visiting the United States.
China’s economic development is entering a new stage of independent research and development, with multiple measures in effect simultaneously, such as introducing foreign capital, sending students overseas, conducting online learning and exchanges. In other words, giving play to comparative and late-mover advantages at the same time. Meanwhile, the influence of independent innovation mechanism is growing, which pushes and demands us to move on with technological innovation and reform the innovation system. The recent Sino-US trade friction has been a perfect reality check for China. The development of scientific research in United States is closely related to property rights. The implementation of Bayh–Dole Act ensures that even within national research projects, personal intellectual property rights will be protected. As a result, it serves as incentive for both researchers and operators, and also allows capitalization and globalization of intellectual property rights. We must give play to both national function, in terms of basic scientific research and underlying technology research, and market’s effect, in terms of incentive mechanism for intellectual property.
- 3. On the new stage of China’s consumption
In the past, low consumption rate and high savings rate were two major economic problems in China. Since 2004, savings rate has exceeded 40%, reached 52% in 2012, and decreased to 44% in 2016. With rising consumption rate, we can expect a general trend which can be attributed to multiple factors. Firstly, the overall income level continues to rise. Secondly, income level of low-income group is growing at faster pace. For example, migrant workers’ income growth rate has been at a steady 17-18% since 2007. Ninety percent of the extra one thousand yuan will be used in consumption, which is a huge stimulus on consumption growth. Thirdly, social security. Fourthly, consumer finance and e-commerce. Finally, consumption by retirees, known as negative savings in economics, also begins to grow as a result from the retirement of the first generation that became rich after reform and opening-up.
We are now facing two turning points. First, high-tech investment has become critical after entering the stage of independent innovation. Second, the ones that are considered as emerging industries in China are developing rapidly, such as growth in general consumer goods, leisure, fitness, health care, medical treatment, vacationing, spiritual and cultural consumption. The return on both aspects are considerable, making them ideal and important areas for investment. In this sense, China will not lack investment opportunities.
 Author: Fan Gang, President of CDI
Author: Fan Gang, President of CDI
Editor’s Note: Prof. Fan Gang gave a speech at the first Summit Forum on Financial Risk Prevention which was held in Shanghai. During which, he analyzed the significance and influence of prevention and control of financial risk from macroscopic perspective
Financial risk and debt risk are very serious problems, which should be approached carefully without unnecessary exaggeration since they are still controllable and do not entail immediate financial crisis.
First, the risk in lack of government regulation. Certain basic problems that should have been controlled through financial market regulation are only regulated after lengthy delay, and until being proposed on the Central Committee meeting. As a result, market risk escalates. Such situation should be prevented and resolved.
Second, financial risk in the government. After implementing the stimulus policy in 2009, local financing platform’s annual total amount of financing rose from RMB one trillion to seven trillion. With the steep increase, we need to tighten control on this type of government financing risks.
Third, risk in state-owned enterprises. The debt ratio of state-owned enterprises is relatively high, reaching 68%. In addition, there are many “dead” enterprises, which are difficult to handle.
Fourth, risk in private enterprises. One contributor to the overheated economy seen in recent years is the massive amount of companies. Underneath them, is corporate debt. It is necessary to merge and reorganize these companies seen in various industries, so as to reduce industrial concentration, reduce the total number, in order to expand the scale and improve efficiency of the industry, and essentially letting the industries better develop. Nonetheless, if no action is taken, it may lead to earlier onset of financial crisis.
We need to treat these financial risks seriously, in each node and all industries, in order to improve the quality and efficiency of our economy as a whole.
 Author: Fan Gang, President of CDI
Author: Fan Gang, President of CDI
Editor’s Note: Opening up is in line with China’s fundamental interests. A new round of reform and opening up will certainly create more opportunities for China’s development.
Opening up is in line with China’s fundamental interests. Since 1978, China has achieved rapid economic development by opening up its market and introducing foreign investment. China is now implementing the “going global” strategy, which means it will open even wider in future. It will contribute to China’s long-term interest which is to achieve mutually beneficial cooperation in the opening up.
Recent years have seen the retreat of globalization. Under such circumstances, China shall first have a clear understanding of its fundamental interests, which lie in sustaining long-term growth and closing the gap with developed countries. China shall steadily press forward with economic restructuring as it opens wider, for instance, by conducting supply-side structural reform, cutting overcapacity and excess inventory, deleveraging, and defusing financial risks. China should also maintain a prudent monetary policy to ensure steady economic growth.
 Author: Fan Gang, President of CDI
Author: Fan Gang, President of CDI
Editor’s Note: The Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area hinges on the concept of metropolitan area and the coordination of different mechanisms. The establishment of the “2+3” free trade area consisting of Nansha, Qianhai, Hengqin, Hong Kong and Macao will promote the development of the Bay Area.
Metropolitan areas provide impetus for China’s urbanization, industrialization and innovation-driven growth since they have emerged as a solution to urban challenges like housing, traffic and employment. The Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area will be a major driving force for China’s development.
There is a great chance to establish a free trade zone alliance inside the Bay Area while Hong Kong and Macao tariff-free zones are already in the region. In addition, Guangdong has three pilot free trade zones, Nansha, Qianhai and Hengqin. It will be an innovative move to join Hong Kong, Macao, and the three free trade zones, to form the “2+3” free trade area. Once the alliance is established, the development of the free trade area will be facilitated so does the Greater Bay Area as a whole.
The Bay Area will continually unleash potential and upgrade economic structure, with an increasing share of the high-end service sector and emerging industries such as digital economy, life sciences, aerospace, renewable and sustainable energy, etc. It will become a global international trade center for goods and services.
 Author: Cao Zhongxiong, Executive Director, New Economy Research Department
Author: Cao Zhongxiong, Executive Director, New Economy Research Department
Overview: Mobike’s acquisition and Didi Chuxing’s dilemma mark that the sharing economy is entering its difficult times. In the future, the mobile transportation platforms need to think about how to make profits; otherwise they are doomed to be merged.
The sharing economy can integrate all kinds of dispersed idle resources, solve the problem of asymmetric information, and accurately find diversified demands, so that the resources can be efficiently reallocated. However, concern about the prospect of the sharing economy has been exposed by the acquisition of Mobike and Didi Chuxing entering a difficult time.
Mobike’s acquisition and Didi Chuxing’s dilemma show that the sharing economy is faced with three difficulties: firstly, it starts with “free user charge” and might be ended by “free user charge”; secondly, it excessively pursues the user growth; thirdly, it only focuses on financing instead of making profits.
The mobile transportation platforms need to operate as an enterprise. Firstly, the sharing economy enterprise must be profitable. Secondly, the sharing economy needs to reduce its operating costs. Thirdly, the sharing economy needs to be regulated by authority when it involves with social benefits and consumer protection. As long as the mobile transportation platforms create sustainable revenue, the integration can be avoided.
 Author: Fan Gang, President of CDI
Author: Fan Gang, President of CDI
Editor’s Note: Impelled by the anxieties over China’s economic rise, United States has initiated a series of actions towards China, including the trade war and possibly with investment and intellectual property as targets. China shall actively respond to these actions with long-term development interests in mind.
The current trade frictions between China and the United States have not yet escalated to a trade war, although both sides are “preparing” for one. There are several issues that should be looked at properly.
With increasing anxiety over China’s economic rise and change in world economic landscape, United States now intends to contain China’s development by targeting intellectual property and imposing restrictions on high-tech exports in the name of “reducing trade deficits”.
Two issues need to be made clear regarding Sino-US trade imbalances.
First, before being assembled in China, 90% of parts are not produced in China, but are rather imported from other Asian countries as part of the production chain. In other words, much of China’s trade deficit will end up as trade surplus with the US.
Second, at certain points nearly 60% of exports are derived from multinational corporations in China. Some products were produced by American multinational corporations in China and exported to United States, in which case China’s profits were rather low. American consumers have benefited from high-quality and reasonably priced products made in China. The US has also enjoyed a relatively low inflation rate. The US government, however, has failed to properly examine this issue, only focused on the impact of China’s rise on the US instead.
Since China is part of the global production chain, in the long run the trade war will certainly have negative effects on China and the US as well as other countries that are part of the production chain.
China’s biggest interest is sustained development. As a late starter, China should be fully aware of the difficulties during development despite fast economic growth over the past 40 years. To maintain sustainable growth, China needs to keep long-term interests in mind and minimize external disturbances through rational counter measures.
More...
 Author: Hu Zheng, Invited Researcher of CDI, Director of China Merchants Group, and Chief Representative of China Merchants Group in Central Asian and Baltic Region
Author: Hu Zheng, Invited Researcher of CDI, Director of China Merchants Group, and Chief Representative of China Merchants Group in Central Asian and Baltic Region
Editor’s Note: The implementation of the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) shall be closely combined with the reform and opening up, top-level design, shared development, sustainability. Construction of overseas industrial parks is the highlight of BRI. In the new era, the emphasis of BRI is to properly deal with the relationship between “Going Out” and “Bringing In”.
The implementation of BRI deepens China’s reform and opening up and they are closely integrated with each other. In the course of reform and opening up that started since 1978, the most prominent feature is “Bringing In”. The establishment of special economic zones, high-tech parks, bonded logistics parks, free trade zones and the introduction of capital and technology have directly driven the leapfrog development of China’s economy and have also exerted significant impact on the world.
Under the context of the reform and opening up and with the advancement of BRI, the “Going Out” is endowed with new characteristics. First is the support of national strategies and policies. Second, we should focus on addressing top-level design issues such as policy coordination, infrastructure connectivity, trade, currency and people. Third, we should uphold the concept of shared development. Fourth, we should aim at sustainable development. Chinese enterprises should innovate and create a new model of Going Out.
Construction of overseas industrial parks is the highlight of BRI and has gained high recognition from countries along BRI. The construction of parks will not only drive local economic development and promote local employability, but also facilitate the transformation and upgrading of production capacity. Overseas industrial parks have become the strategic pillar of BRI and provided Chinese enterprises with a new platform of win-win cooperation.
In the new era, the implementation of BRI should be promoted with the spirit of reform and opening up. In this process, we should adhere to the concept of win-win cooperation, properly handle the relationship between “Going Out” and “Bringing In”. That means China should export its own development experience and learn from others at the same time, which will greatly enrich the connotation of BRI. In addition, we should value sustainable development and share mutual benefits while implementing BRI.
 Author: Fan Gang, President of CDI
Author: Fan Gang, President of CDI
Editor’s Note: Eventually, China and the United States will need to sit down at the negotiating table to solve trade frictions.
Trump would sooner or later impose trade sanctions on China, but no one had expected such a big move. China’s exports to the United States amounts to over 400 billion U.S. dollars, while Trump is now seeking to impose tariffs on up to $60 billion of Chinese imports. Such a big move on trade shows that the United States treats China as its primary rival in trade. The action also illustrates that such superpower like United States can be brutal sometimes, adopting measures without any evidence or reasonable analysis and ignore rulings by the WTO.
American consumers will be the victims of trade war between the US and China. The trade war will also harm China as the consumer product prices could rise. It is necessary for China to consider the price elasticity of demand when deciding how much to export. Generally speaking, the trade war will impact on United States as much as China. There is the fear that if you want to fight this trade war and I do not fight back, you would probably be even less reasonable tomorrow. Thus, China will certainly take countermeasures.
Keep a level head in face of US-China trade war
As a rising middle-income country, China needs to be prepared for the possible suspicion, antagonism and even aversion from others. These reactions must be taken care of proactively but also with a cool head. This is not the first time for China to meet with oppositions from other countries, nor will it be the last. China shall keep a level head in face of the cacophony of voices as it rises.
Those who in the past believed the China’s growth depended on low-end manufacturing have now discovered that China is able to innovate and has even become a leader in certain high-tech industries. The western world now feels threatened as China becomes a stronger competitor. And the trade war is highly interconnected with the rise of rise since Trump has declared that the trade sanctions on China are to protect US interests.
China has worked hard for its own success. Chinese have lower per capita income but are increasingly capable of innovation. Most exporters in China are private companies not subsidized by the government. There are many foreign-funded products and services among Chinese exports as well, for example, products that are manufactured in China by American businesses, which also count as Chinese exports to the US when calculating the US trade deficit with China.
Structural conflicts exist in Sino-US trade
The Sino-US trade frictions is not simply caused by trade deficit but more fundamental structural challenges existing in the two kinds of economies. Initially, the US alleged that the deficit due to China’s low foreign exchange rate. However, trade deficit has persisted after China raised RMB’s exchange rate against the US dollar. Even after US conducted the 301 Investigation against China, trade deficit still stayed on the same level.
China is not only highly competitive in a wide range of industries and also benefits from low cost and high efficiency in many fields. Even though, the competitivity in high-tech industries still needs to improve. Structural problems exist in Sino-US trade in the sense that China is not allowed to import the desired products as it exports its products to the US.
Stand up to US-China trade war
First, China needs to have reciprocal countermeasures. China will probably raise tariffs in response to the imposed higher tariff, which is something that China is capable of doing. Second, crisis management consciousness is crucial to preventing potential risks from developing into full-fledged crises. China needs to negotiate and defuse tensions where possible to avoid a completely hostile situation. Third, China-US trade only accounts for just 16-17% percent of global trade, and trade with Europe, another 16-17%. China also has the option to develop trade relations with emerging countries, including countries in Latin America, Middle East and Africa.
China’s core concern is still development. China welcomes foreign investment not just for the sake of attracting capital, but also creating jobs and bringing in advanced technologies and management. We observe how foreign-funded businesses operate and learn their experience in management. This is not stealing, as this kind of knowledge or expertise is universally shared. It is a common practice among all countries to model on existing products and come up with similar products on their own, not just in China. China is committed to staying open and will not shut its door for foreign businesses even though its own businesses are denied entry into a foreign country.
Globalization will not stop
Globalization was started by American capital and multinationals in the first place. American workers did not take it seriously at the beginning, but globalization has indeed spurred the development of China. As farmers leave villages to work in cities, China has seen a steady increase in per capita income, fast development of technologies and larger exports. Naturally, discontent in the US rises as local workers lose jobs to their foreign counterparts. In a sense, reversals and relapses in the process of globalization are inevitable. It is therefore important to anticipate challenges and be prepared.
However, globalization will not stop. Multinationals from developed countries now continue to promote globalization as they are still establishing their presence across the world today to maximize their gains. Two new forces have also joined to promote globalization nowadays, one being low-income countries which have discovered the benefits of attracting foreign investments for their own development from the experience of China and India, the other being middle-income countries like China.
China, as a middle-income country, needs globalization in the process of bringing in foreign capital and encouraging its businesses to go global. Going global is a must for China in view of its domestic excess of capital. Despite a moderate level of income in China, the high savings rate has resulted in a huge amount of capital, which will lead to overcapacity if invested within the country. Many Chinese businesses have also come to realize the importance of seizing the opportunity to develop abroad as China restructures its economy, thus starting to allocate global resources.
Despite opposing voices, globalization will continue in the long run. It is natural that the US wants to get some of its businesses back to accommodate the interest of domestic workers, as all governments wish to see more investment within their own borders. While there are many reasonable ways to do this - reducing interest rate in particular - fighting a trade war, however, is a bit of reversal of globalization.
 Author: Liu Muyun, Invited Researcher of CDI and President of Beike Biotechnology
Author: Liu Muyun, Invited Researcher of CDI and President of Beike Biotechnology
Editor’s Note: Zero tariffs alone cannot address the root cause of exorbitant prices of imported anticancer drugs and much more should be done to expand market access to quality anticancer drugs.
When he held a news conference at the end of the two sessions, Premier Li Keqiang said that tariffs on drugs will be slashed, while the much-needed anticancer drugs might phase in zero tariffs. However, zero tariffs alone cannot address the root cause of exorbitant prices of imported anticancer drugs.
It can achieve a scale effect for international pharmaceutical companies to concentrate the large market demand of China, negotiate directly with the producers via a national channel and purchase anticancer drugs in bulk. National procurement does not only mean lower prices, but also quality assurance. It is feasible to set up a centralized procurement platform at the national level with a new state administration on medical insurance to be put into place according to the State Council institutional reform plan of 2018.
We should give play to the role of Internet, establish an evaluation database for anticancer drugs, a catalogue of much-needed clinical drugs, a database to optimize catalogue and price negotiations of the centralized procurement.
In addition to scientific and technological innovation, mechanism innovation is also needed. We should reform the management of clinical tests, speed up the review and approval system for innovative drugs, accelerate application and marketization of research results, improve the business environment generic drugs, and combine technological innovation with clinical diagnosis and treatment.
The key role of medical service in the treatment of complicated diseases should also get enough attention. Innovative drugs, surgery and therapy are all clinical diagnosis and treatment tools; however, people who use these tools efficiently and economically also matters. Health practitioners deserve recognition and respect from the society.
 Author: Fan Gang, President of CDI
Author: Fan Gang, President of CDI
Editor’s Note: “As an economist, I am very proud of achievements of China’s economy. However, it is crucial to keep a realistic and sober amidst the chorus of praise. There will be something wrong if we do not address problems facing China’s economy,” said Prof. Fan Gang.
Recently, especially since the beginning of 2018, public opinions in domestic and abroad have seen a great change from the previous decries to the current praises. The cover story in Time was titled “China won” and domestic opinion leaders also started to applaud the rise of China. It is however crucial to keep a realistic and sober amidst this chorus of praise.
Indeed, China has made great strides, especially in manufacturing. A short documentary made by KJ VIDS, a British media company, mentioned that by 2005, the construction area of China in every two weeks is as big as today’s Rome. Moreover, the production value was able to create one Greece every 16 weeks and one Israel every 25 weeks. Despite these great achievements, we need to be aware of the existing problems. For example, China’s per capita GDP in 2017 was 9600 US dollars, making China rightfully a middle-income country. However, it was less than 20% of that of the United States. Problems will arise without a sober mind towards addressing our weaknesses.
One neglected achievement is that China’s economy has maintained high growth rate in 40 years with no crises, which is unprecedented in the world. Developed countries, in the early years of rapid development, saw economic crises every 10 years or so. China’s economy also has its cycles, with highs at around 14% and lows at 6%. What has made China’s economy unique in the world is that it has never experienced major economic crises or recessions. This is partly due to lessons learned from the bursting of bubbles and financial crises experienced by developed countries over the past four decades.
Economic landscape and growth of China
China’s economy went through a cycle in the 1990s, got over-heated from 1992 to 1994, experienced a five-year downturn from 1995 to 1999 and remained mired in a soft patch from 2000 to 2002 until finally recovering after the SARS outbreak in 2003. The second overheating came in 2005 and lasted till 2007. China went through a self-imposed restructuring as the world was hit by a financial crisis in 2008, and saw a periodic peak between 2009 and 2010 due to economic stimulus. Another downturn was experienced from 2011 onwards until the economy touched the bottom in 2016 and started to warm up slightly in 2017; however, the economy was not bouncing back and would still stumble at the bottom for a while with certain unsolved issue.
In the short term, China’s economy will maintain a 6.5-7% growth rate with a neutral macroeconomic policy without either stimulus or tightening, which will facilitate ongoing reform and restructuring before entering the next round of growth. It is thus important to see economic growth from a periodic point of view, and regard economic downturns as fluctuations. One thing that is worth noting is that it takes longer for China’s economy to complete the process of soft landing than to restructure during crises. In the long term, we should be fully aware of the challenges facing China’s economy, including rising labor and environmental cost, a widening income gap and a global landscape under newly emerged risks.
Potential is huge too, with per capita GDP at only 9000 US dollars, industrialization rate less than 70% and 30% of the labor force living primarily on agricultural income. Only 55% of Chinese people lives in cities and 70% of the population are low-income people, half of whom being farmers and half being migrant workers. Overall, China has low levels of consumption and high savings rate, with family consumption representing a mere 30% of the GDP. We shall have confidence in exploring this potential.
Changes in global landscape
External environment is a major source of uncertainties at present. Positively, developed countries have seen strong recovery driving China’s exports. The Federal Reserve has raised interest rates and then China introduced a combination of policies by raising interest rate and lowering required reserve ratio, which remained neutral.
The “Trump effect” has indeed contributed to the rise of protectionism. What Trump does remind governments around the world of the need to reduce tax burdens on businesses, which is good. He deems that Chinese government has been correct in taking advantage of other countries for the interest of Chinese people, while the US government has failed to do so for the interest of its people, which is why he tries to make up for this gap. In future, he is likely to take measures in trade.
Does this mean a retreat of globalization? At first, globalization was advocated by developed countries. Their governments represented the interest of multinationals and domestic capital to promote globalization around the world. After realizing that globalization was against their interest, their domestic workers protested against this trend. However, at present, multinationals with global presence are still playing a crucial role in allocating resources worldwide as the drivers of globalization. A decade ago, developing countries had reservations about globalization, as they feared over the prospect of being dominated by multinationals and losing opportunities for job growth. Later on, however, as they found globalization actually contributed to their economy, they, including China, turned to be advocates of globalization.
China wishes to continue to attract foreign capital to gain know-how for its own development and many policies recently rolled out by the Chinese government encourage foreign capital to enter China by improving business environment. At the same time, China has also entered the stage of going global. High savings rate over the past two decades has accumulated a significant amount of capital, which will only lead to excess capacity if invested in the domestic market. Therefore, Chinese businesses should now compete in the world market and utilize global resources to seek new growth engines. China benefits from and advocates globalization, which will certainly continue to grow despite such setbacks as the rise of trade protectionism and short-term retreat.
New growth momentum
First, business environment. China’s policies are increasingly pro-innovation and pro-entrepreneurship, with more tolerance of problems that might arise from innovation. For instance, the messy outcome of bike sharing is unimaginable in many countries, but is treated with tolerance in China. In China, new things get a chance to survive, and when there is a problem, supervision follows. In the next few years, a big share of China’s growth will come from innovation and entrepreneurship.
Second, the development of financial systems, especially direct financing mechanisms. In the past, businesses took out loans from banks, but now they have more options, such as venture capital, PE, or selling equities. Finance plays a fundamental role in spurring innovation and entrepreneurship and the development of the financial system will come as an engine for economic growth in future.
Third, consumption growth. In the past, people born in the 1980s and 1990s used to be the main force of consumers, while retirees, who had little disposable income, spent very little. Things are different today. The wealthier generation begins to retire, and with both time and money, starts to consume more, transforming the country’s consumption pattern.
Fourth, manufacturing development. The improved quality of some Chinese manufacturers will contribute to a stronger image of “made in China”, instead of being a synonym for shoddy products. With improved consumer confidence in our products, the manufacturing sector will embrace a new round of growth.
Industrial development
First, that all industries have potential for growth does not mean all enterprises enjoy the same prospects, as they would experience constant mergers and restructuring. In the end, big enterprises will become even bigger and small enterprises will get merged into bigger ones. Enterprises shall fully consider how they would be merged so as to improve their production and innovation capacity. Research on the overcapacity in the steel industry in the American history suggests that the cause is vicious competition for resources among private enterprises during rail construction. J.P. Morgan played a dominant role in the mergers of the US steel companies with over 700 companies organized the steel industry and 200-300 companies out of business, which is a classic example of mergers. Trump once said that he enjoyed economic slumps when is a good time for mergers. Mergers and acquisitions are the destiny of many businesses. This is a good thing, as businesses can channel the return on investment into new undertakings.
Second, the manufacturing sector still has huge potential. In the 1980s, Korea was concerned about the industrial hollowing-out effect, worried that it would experience recession when industries move to China. However, the Korean economy has proved otherwise, gradually advancing to high-end growth. This rule also applies to China. We will be able to move forward as our manufacturing sector continues to climb the value chain.
Third, application of new technologies, and in particular, the internet. The internet is a public technology and serves every individual, company and industry, which makes it crucial for industries to keep pace with the information trend.
Fourth, professionalism and dedication. Successful companies are invariably those that are dedicated to their businesses and persevere for a long time, a quality that is indispensable in pursuing craftsmanship and an upgraded version of “made in China”.