Financial Centre Futures Webclave 2025 - Current Challenges And Strategic Solutions
Information

Information
The meeting was organized by Z/Yen Group in partnership with China Development Institute to bring together representatives of financial centers across the world to consider current strategic questions. This was the fifth annual webclave for financial centers, having started during the pandemic. The meeting focused on:
- Current Challenges – what are the challenges that are financial centers’ current priority?
- Solutions – where are financial centers placing efforts for development?
Date and time: 15:00-17:00 Beijing Time (GMT+8), 24 July 2025
2025 Shenzhen Hong Kong Cooperation Forum
Information

Information
The Sino-US trade war continues to exert profound impacts on the global supply chain landscape. As core cities within the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, Hong Kong and Shenzhen should proactively explore collaborative pathways for supply chain restructuring to enhance regional economic resilience. Concurrently, against the backdrop of digital economy advancement and consumption upgrading, the cultural, creative and tourism industry has emerged as a new engine driving economic growth.
With this in mind, China Development Institute and One Country Two Systems Research Institute jointly organized the 3rd Shenzhen Hong Kong Cooperation Forum on July 11, 2025. Centered on the dual themes of "Supply Chain Restructuring" and "Cultural Tourism Industry Innovation," the forum convened experts and scholars from both cities to jointly strategize synergistic development approaches.
Date: July 11, 2025
Hosts: China Development Institute, One Country Two Systems Research Institute
Venue: The Hong Kong Polytechnic University
Korea Legislation Research Institute Delegation Visits CDI

Date: May 26, 2025
On May 26, 2025, Prof HAN Yeong-Soo President of Korea Legislation Research Institute led delegation to CDI. Discussion focused on how Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area provided legislative support for science and technology research and innovation and explored legislation innovation amidst the quickly evolving economic landscape. CDI experts briefly introduced the development of Shenzhen Special Economic Zone as well as future prospects. Two sides also exchanged views on the development of public policy research think tanks in both China and South Korea.
Policies Ensured Overall Stable Economic Performance, Pursuit of Better Life to Drive Domestic Demand

Date: July 20, 2025
In the first half of 2025, China faced growing external turbulence alongside interwoven domestic challenges. Despite these pressures, the economy demonstrated overall stability and continued progress in high-quality development. Tariff tensions eased following May’s negotiations in Switzerland, reducing potential impacts on export sectors. Coupled with domestic policy support, economic activity showed signs of recovery, though challenges persisted. Moving forward, policy implementation acceleration is needed to enhance multiplier effects, while domestic demand to be expanded by leveraging people’s aspirations for a better life.
The Economy Operated with Overall Stability.
In H1 2025, GDP grew 5.3% y/y at constant prices, 5.4% in Q1 and 5.2% in Q2. Value-added output rose across primary, secondary, and tertiary industries in Q2. Service industry remained a key growth engine, expanding 5.5% y/y in H1, with information transmission, software, and IT services leading at 11.1% growth. June’s Manufacturing Production Index and New Orders Index both increased m/m, signaling accelerated output and improved demand.
Tariff Tensions Disrupted Export Trends.
H1 goods exports rose 7.2% y/y in RMB terms, up 0.3 pp from Q1 and exceeding 2024’s performance, mostly due to 2024’s low base and tariff war effects. Following May’s Sino-U.S. tariff reductions, the y/y decline in U.S.-bound exports narrowed from -34.5% in May to -16.1% in June. Meanwhile, China maintained robust export growth to re-export hubs in June. Exports to ASEAN and Hong Kong SAR accelerated m/m. With pent-up U.S. orders fulfilled and given increased scrutiny of re-exports in U.S. trade agreements, future exports could face pressure.
Industrial Output Growth Accelerated Y/Y.
H1 industrial value-added for enterprises above the designated size rose 6.4% y/y, 0.6 pp higher than full-year 2024. Q1 and Q2 saw 6.5% and 6.3% growth respectively. Key drivers included: expanded large-scale equipment upgrade and consumer goods trade-in programs releasing domestic demand; and digital, smart and green transition in industrial development, notably digital product manufacturing went up 9.9% y/y, outpacing industrial averages for 23 straight months.
Investment Growth Decelerated Y/Y.
H1 fixed-asset investment grew 2.8% y/y, down 0.9 pp Jan–May. By sector, infrastructure went up 4.6% y/y (down 1.0 pp Jan–May), manufacturing up 7.5% y/y (down 1.0 pp Jan–May), real estate down 11.2% y/y (down 0.5 pp Jan–May) reflecting persistent stabilization pressures. While large-scale equipment upgrade and consumer goods trade-in programs continued to drive strong growth in high-end, smart, and green manufacturing, investment growth slowed post-acceleration across all three sectors.
Trade-in Policy Accelerates Consumption.
Driven by a series of policies aimed at promoting consumption, domestic demand continued to increase. H1 retail sales rose 5.0% y/y, up 0.4 pp from Q1 and continuing quarterly acceleration since Q3 2024. June sales grew 4.8% y/y, down 1.6 pp m/m. The implementation and optimization of consumer goods trade-in program boosted goods and services consumption, demonstrating strong momentum. H1 service retail picked up pace and rose 5.3% y/y, up 0.3 pp compared to Q1. Policy sustainability and consumption impacts warrant monitoring.
Pushing Prices Toward Higher Levels.
H1 CPI averaged -0.1% y/y, unchanged from Q1. Monthly volatility stemmed from Chinese New Year timing seen in CPI increased 0.5% in January, then decreased 0.7% in February. March–May CPI decline narrowed to -0.1%, before turning positive in June (up 0.1% y/y) due to international commodity price fluctuations and domestic consumer demand stimulus policies. The narrowing decline in food prices and the expanding growth in service prices are the main contributors to Q2’s improvement. H1 PPI fell 2.8% y/y, continuing its downward trend pressured by seasonal drops in prices across certain domestic raw material manufacturing industries, lower energy prices driven by increased solar, wind and hydropower generation, and price pressures faced by some export-led sectors.
Image source: IE Insights (2022). https://www.ie.edu/insights/articles/our-urban-life-in-2022/
Former Lord Mayor of the City of London, Prof. Michael Mainelli, Visits CDI

Date: March 31, 2025
On March 31, 2025, Prof. Michael Mainelli—British economist, former Lord Mayor of the City of London, and Chairman of Z/Yen Group—visited CDI. Prof. Mainelli shared insights on Z/Yen’s recent projects, including efforts to reduce trade barriers, initiatives to support the global green transition, research on the Smart Centres Index, and programs promoting Sino-UK educational exchange. The two sides discussed potential opportunities for bilateral cooperation between China and the UK, as well as prospects for research collaboration between CDI and Z/Yen.
Economic Recovery Gathers Pace Amid Policy Support and Structural Shifts

Date: March 20, 2025
Following the Spring Festival, economy regained momentum in February as businesses resumed operations, accelerating production and commercial activity. Key indicators such as the Manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI), Non-Manufacturing Business Activity Index, and Composite PMI Output Index all rebounded month-on-month, remaining in expansionary territory. While these figures signal a tentative recovery from earlier lows, sustaining growth will demand stronger policy reinforcement and expedited implementation.
Economic Recovery Shows Marginal Improvement from Low Levels
In February, the Composite PMI Output Index rose by 1.0 percentage points from the previous month to 51.1%, returning to expansion territory. The Manufacturing PMI, up 1.1 percentage points to 50.2%, emerged as the primary growth driver. A breakdown of the index shows that both production and demand within the manufacturing sector improved, with the Production Index and New Orders Index rising by 2.7 and 1.9 percentage points, respectively, to 52.5% and 51.1%. Both indices entered expansion territory, indicating a notable improvement in manufacturing supply and demand. This resurgence bolstered corporate confidence, pushing the Purchasing Volume Index up by 2.9 percentage points to 52.1%. On the non-manufacturing side, the Non-Manufacturing Business Activity Index edged up 0.2 percentage points to 50.4% in February.
Export Disruptions Due to Tariffs and "Front-Loading"
From January to February, Merchandise exports grew 3.4% year-on-year, though this was a slight moderation compared to full-year 2024 and December figures. Trade with the U.S. expanded at a slower pace, with exports rising 2.9% year-on-year—5.1 percentage points lower than in December 2024—partly reflecting adjustments to U.S. tariff hikes. Meanwhile, shipments of products that retain a competitive edge under current tariff conditions, such as smartphones and laptops, saw a boost, possibly as exporters sought to stay ahead of potential U.S. trade restrictions. However, taking into account two fewer working days in January-February 2025 compared to the same period in 2024, the year-on-year export growth rate would have been higher if measured on a per-working-day basis.
New Growth Drivers Accelerate Industrial Expansion
Industrial output from large-scale enterprises grew 5.9% year-on-year in January-February, extending the robust momentum seen since Q4 2024. The pace edged up 0.2 and 0.1 percentage points from the fourth quarter and full year of 2024, respectively. Externally, export momentum sustained industrial expansion, with export delivery values rising 6.2% year-on-year—1.1 percentage points faster than 2024’s annual rate. Domestically, policies such as large-scale equipment upgrades and consumer trade-in programs, expanded in 2025, spurred industrial modernization and unlocked consumption potential, further driving growth. On the supply side, equipment manufacturing and high-tech industries led the charge, with rapid growth continuing to optimize the industrial structure.
"Two Major" Projects Fuel Investment Growth
In January and February, investment increased by 4.1% year-on-year, up by 0.9 percentage points compared to the whole of last year. First, support for "Two Major" projects (advancing national strategic initiatives and enhancing key security capabilities) has strengthened, with physical work volumes picking up, driving a faster growth in infrastructure investment. Infrastructure investment rose by 5.6% year-on-year in January and February, accelerating by 1.2 percentage points from 2024, contributing 1.1 percentage points to overall investment growth. The "Two New" policies (promoting large-scale equipment upgrades and consumer goods trade-ins) have been further expanded, with their effects becoming increasingly evident, spurring rapid growth in equipment investment. Second, progress in the high-quality development of key industrial chains is solid, with the transformation of traditional industries accelerating, leading to strong growth in manufacturing investment. Third, real estate policies have mitigated the decline in investment, showing early signs of stabilization.
Trade-In Programs and Green Consumption Boost Retail Sales
In January and February, retail sales grew by 4.0% year-on-year, with goods retail increasing by 3.9% and catering revenue rising by 4.3%. The growth in consumer spending was driven by the expansion of trade-in policies, which quickly unlocked demand for appliances and electronics. Meanwhile, the increasing focus on green and health-conscious products fueled strong growth in the eco-friendly and wellness sectors. Additionally, a surge in travel and leisure activities led to a rapid increase in spending on transportation, accommodation, and related services, highlighting a broader recovery in consumption.
Efforts Needed to Stimulate a Balanced Price Recovery
In February, China’s Consumer Price Index (CPI) fell 0.2% month-on-month and 0.7% year-on-year, reflecting the combined impact of Chinese New Year timing, holiday effects, and volatile global commodity prices. The year-on-year decline was primarily driven by a high base effect: food and service prices surged during February 2024’s holiday period, inflating the comparison base and putting downward pressure on this year’s figure. Food prices dropped 3.3% year-on-year, accounting for over 80% of the CPI decline (contributing 0.6 percentage points to the total 0.7% drop). This sharp contraction in food costs—the largest drag on prices—tipped the CPI into deflationary territory. Meanwhile, the Producer Price Index (PPI) continued to decline due to seasonal industrial sluggishness and softer global commodity prices. However, both month-on-month and year-on-year PPI decreases narrowed by 0.1 percentage points, signaling easing deflationary pressures.
Growth Momentum Moderates, Highlighting Need for Accelerated Policy Support

Date: Feb 20, 2025
In January, due to the Spring Festival holiday and seasonal factors, industrial production entered an off-season, with the Producer Price Index (PPI) declining month-on-month. However, service and food prices rose significantly affected by the timing of the holiday, along with a rebound in gasoline prices, collectively driving an expansion in the Consumer Price Index (CPI) year-on-year growth. Overall, despite signs of moderation, economic activity remains on a positive trajectory, underscoring the need to expedite the implementation of supportive measures
Economic Growth Moderates, but Certain Sectors Gain Momentum
In January, the Composite Purchasing Managers’ Index fell by 2.1 percentage points month-on-month to 50.1%, reflecting impacts from the Spring Festival holiday and the return of employees to their hometowns. This indicates a broad-based slowdown, though overall economic expansion persists. Driven by the Spring Festival effect, sectors related to residents' travel and consumption—such as road transportation, accommodation, catering, ecological protection, and public facility management—saw their Business Activity Indexes rebound into expansionary territory, signaling greater market vitality. Meanwhile, sectors including air transport, postal services, telecommunications, broadcasting, satellite transmission, and monetary financial services maintained robust Business Activity Indexes above 55.0%, sustaining rapid growth in output.
Surge in Aggregate Social Financing
In January, total social financing increased by 7.06 trillion yuan, up by 586.6 billion yuan compared to the same period last year. Financial institutions issued 5.13 trillion yuan in new RMB loans (including loans to non-bank financial institutions), a year-on-year increase of 210 billion yuan. Structurally, the surge was driven by government bonds and corporate financing, while household borrowing remained weak. Corporate financing hit record highs, with medium- and long-term loans growing further despite a high base. The demand for household short-term loans remained low, likely due to the timing of the Spring Festival. Additionally, the reduced demand for business loans to refinance existing mortgages, following cuts in mortgage rates, weighed on medium- to long-term business loans.
Property Market Prices See Divergent Trends
In January, housing prices in first-tier cities continued to rise month-on-month, whereas second- and third-tier cities saw slight declines, reflecting a clear divergence in trends. Specifically, new home prices in first-tier cities increased by 0.1% month-on-month, though the rate of growth slowed by 0.1 percentage point compared to December. In second-tier cities, new home prices rose by 0.1%, marking the first increase since June 2023, while third-tier cities saw a 0.2% decline. For existing homes, first-tier prices edged up by 0.1%, a 0.2 percentage point slowdown from December, second-tier prices dropped by 0.3%, and third-tier prices fell by 0.4%. Year-on-year, price declines narrowed across all city tiers, suggesting gradual stabilization.
Core Consumption Recovery Emerges as Economic Stabilizer
In January, industrial production remained subdued due to the holiday, with the PPI falling by 0.2% month-on-month and 2.3% year-on-year—unchanged from the previous month's annual decline. Prices in non-ferrous metal mining and processing saw significant increases, while ferrous metal smelting, coal mining, and related industries accounted for nearly 90% of the PPI’s annual decline, contributing 2.11 percentage points. The CPI, however, expanded year-on-year, fueled by holiday-driven service and food price surges along with higher gasoline prices. Notably, the core CPI (excluding food and energy) rose for the fourth consecutive month, climbing 0.5% month-on-month and 0.6% year-on-year, with both growth rates accelerating from December.
Stable Economic Performance in 2024, with Ongoing Policy Support Needed

Date: Jan 20, 2025
Despite external pressures and domestic challenges, China's economy exhibited stability and steady progress in 2024. Targeted incremental policies boosted confidence and facilitated a strong recovery. Export growth decelerated in the first three quarters owing to diminished global demand, although industrial supply chains remained resilient. In Q4, an increase in "front-loading exports" stimulated manufacturing growth, whereas large-scale equipment upgrades and consumer goods trade-in programs maintained ongoing demand and investment in manufacturing. Existing policies, together with new stimulus measures, have spurred local infrastructure investment, though further improvements are required. The recovery in the real estate sector remains sluggish, and its economic contribution has not yet improved.
Overall Economic Stability with Continued Growth.
In 2024, China’s GDP increased by 5.0% at constant prices, with quarterly growth rates of 5.3% in Q1, 4.7% in Q2, 4.6% in Q3, and 5.4% in Q4, indicating a stable upward trend. From Q4 onwards, sustained policy impacts significantly enhanced market expectations and confidence, resulting in positive shifts in both the capital and real estate markets. The service sector grew by 5.8% year-on-year in Q4, an increase of 1.0 percentage point from Q3. The stock market surged, with trading volumes in the Shanghai and Shenzhen markets rising by 126.4% and 124.4% year-on-year respectively, significantly outperforming the first three quarters.
Exports See Consistent Growth.
In 2024, China’s goods exports increased by 7.1%, indicating a rise of 6.5 percentage points from the previous year, significantly contributing to economic growth. In Q4, "front-loading exports" surged, and strong consumption demand in Europe and the U.S. stimulated a resurgence in export growth. In December, exports rose 10.9% year-on-year, representing an increase of 4.0 percentage points from the previous month. The U.S. remained the primary driver of growth, whereas exports to ASEAN increased by 18.9%. Products sensitive to U.S. tariffs, such as automobiles, machinery, auto parts, and textile yarns, saw notable growth. Furthermore, Chinese industrial goods gained global competitiveness, further accelerating export growth.
Manufacturing Fuels Industry Resilience.
In 2024, China’s large-scale industrial enterprises exhibited stable growth, with value-added industrial output rising by 5.8% year-on-year, reflecting a 1.2 percentage point acceleration from the previous year. Manufacturing played a central role, rising by 6.1%, whereas mining and utilities grew by 3.1% and 5.3%, respectively. Policy support continued to advance the manufacturing sector toward higher-end development, with equipment manufacturing increasing by 7.7% and high-tech manufacturing by 8.9%, both exceeding overall industrial growth.
Investment Growth Accelerates with Policy Support.
Fixed asset investment increased by 3.2% in 2024, up 0.2 percentage points over the previous year. Backed by ultra-long-term special government bonds and local government special bonds, major infrastructure projects advanced rapidly, boosting infrastructure investment by 4.4%. Manufacturing investment increased by 9.2%, indicating the sector’s shift toward high-end and advanced industries. Investment in high-tech manufacturing and services grew by 7.0% and 10.2%, respectively. In Q4, targeted policy measures contributed to the stabilization of the real estate market, easing the decline in new home sales and driving the growth in the real estate production index for three consecutive months.
Consumption Growth Requires Further Stimulus.
In 2024, retail sales of consumer goods increased by 3.5%, accelerating in Q3 and Q4, but still below the previous year’s pace. Retail sales of goods rose by 3.2%, whereas dining revenue increased by 5.3%, both below the previous year’s growth rates. Sales at large brick-and-mortar retailers rose by 1.9%, with new retail formats performing well. Policies promoting trade-ins for consumer goods resulted in stronger sales in key categories, including home appliances and audiovisual equipment, which maintained double-digit growth for four consecutive months. Auto and furniture sales returned to positive growth, whereas demand for construction and home improvement materials showed signs of recovery.
Stabilizing Prices and Easing Declines.
In 2024, the Producer Price Index (PPI) decreased by 2.2% year-on-year, narrowing its decline by 0.8 percentage points compared to the previous year. From January to July, the PPI decreased from -2.5% in January to -0.8% in July, driven by rising international crude oil and non-ferrous metal prices, a recovering domestic production sector, and a low base effect. However, in August, a dip in global commodity prices led to a 0.7% month-on-month loss, widening its year-on-year decline. Since September, the impact of policy measures and recovering industrial demand has slowed the PPI's monthly decline, with the index turning positive in November and the year-on-year decrease steadily shrinking.
CDI and Mexican Council on Foreign Relations Jointly Held Seminar
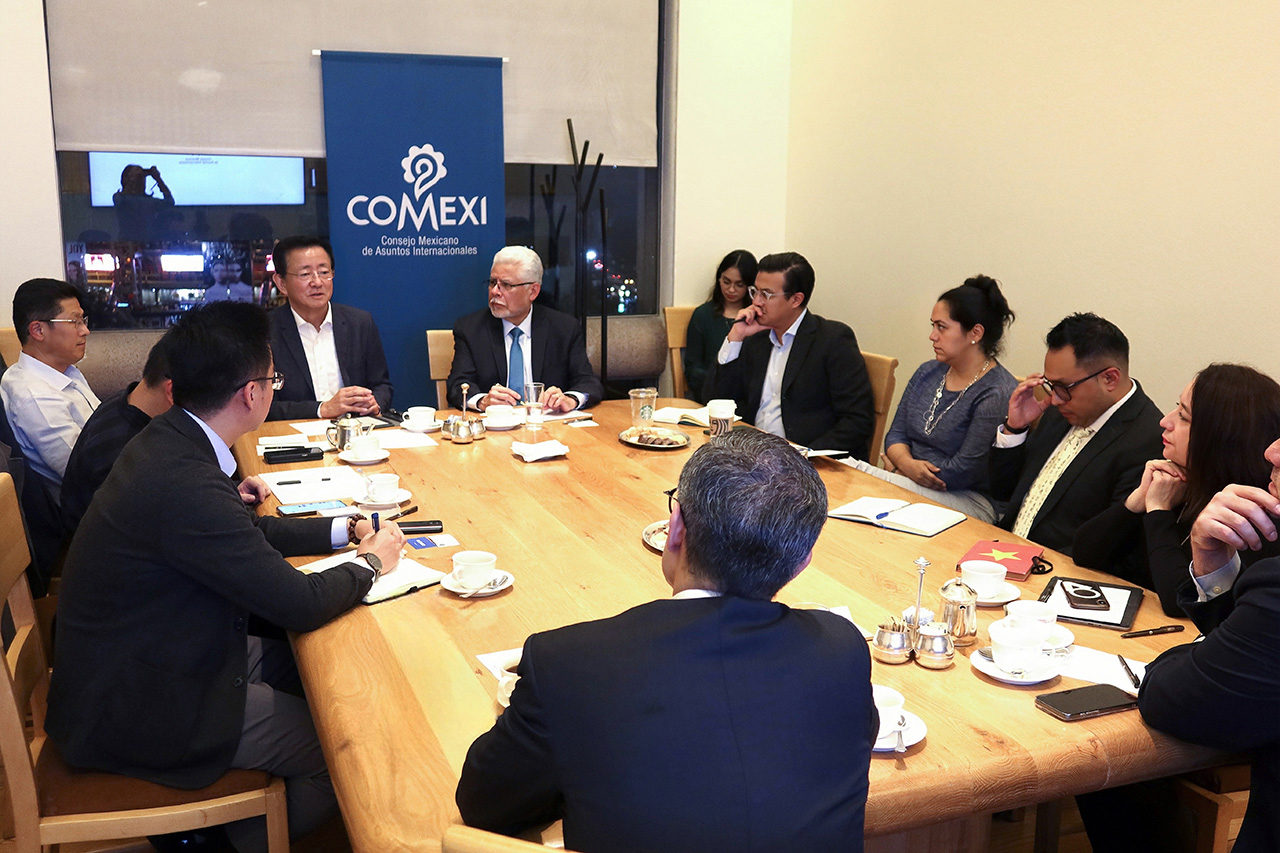

Date: September 12, 2024
During a discussion hosted by the Mexican Council on Foreign Relations and CDI on September 12, 2024, Chinese and Mexican officials, scholars, and entrepreneurs shared insights on the trajectory of Sino-Mexican relations against the backdrop of U.S.-Mexican relations, as well as the opportunities and challenges for Chinese businesses investing in Mexico. The discussion enabled both sides to better understand and prepare for the future landscape of Sino-Mexican trade.
President Fan Gang Visited Chicago Council on Global Affairs and University of Chicago
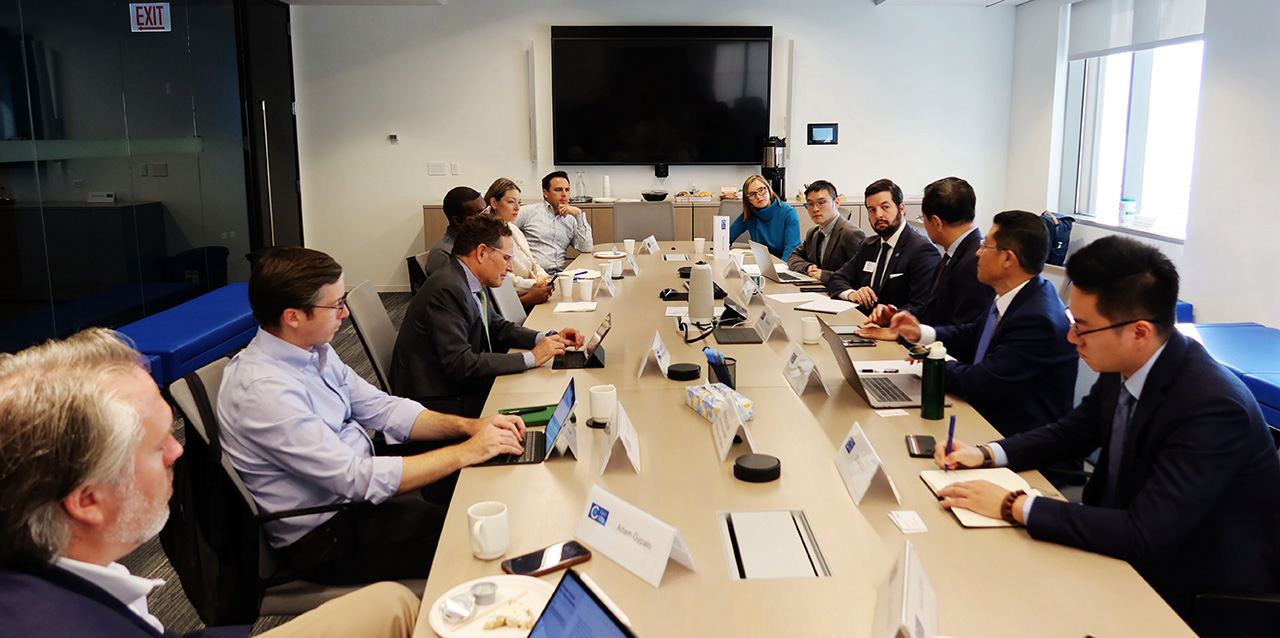

Date: September 10, 2024
CDI delegation led by President Prof. Fan Gang visited Chicago think tanks on September 10, 2024. During the roundtable discussion, Professor Fan addressed China’s economic development and the prospects for U.S.-based international companies operating in China. Academics and business leaders were gathered together to exchange views on the future of Sino-U.S. foreign and trade relations, U.S. trade policies regarding renewable energy industries and supply chains, as well as their broader implications.