Information
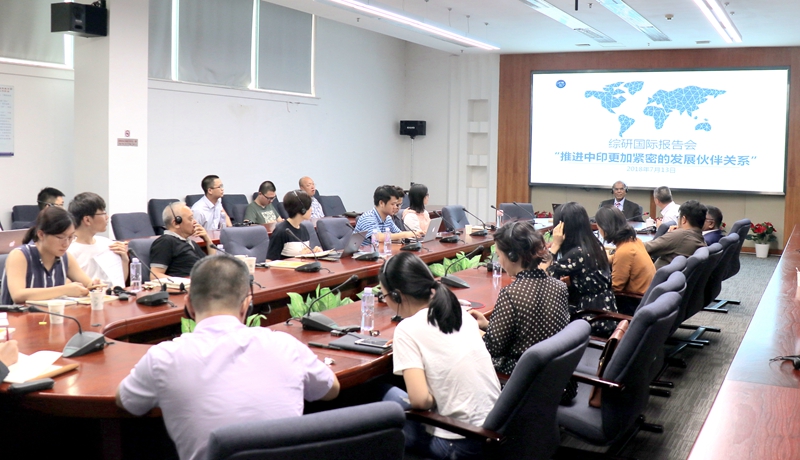 Theme: China-India Cooperation under BRICS Framework
Theme: China-India Cooperation under BRICS Framework
The new decade heralds a golden age for BRICS countries. To promote China-India trade ties in the spirit of pursuing mutual benefits and win-win results will inject new vitality into the China-India relation and cooperation among BRICS countries.
In the context, how can China and India synergize Belt and Road Initiative with Make in India? How can the two developing countries work together to engage into global supply chain and move up on the global value chain? How can they cement cooperation in emerging industries?
Date: July 13, 2018
Venue: Room 101, CDI Mansion, Shenzhen
Host: CDI
Program
Program
14:30-14:35 Opening Remarks
GUO Wanda, Executive Vice President, CDI
14:35-15:35 China-India Cooperation under BRICS Framework
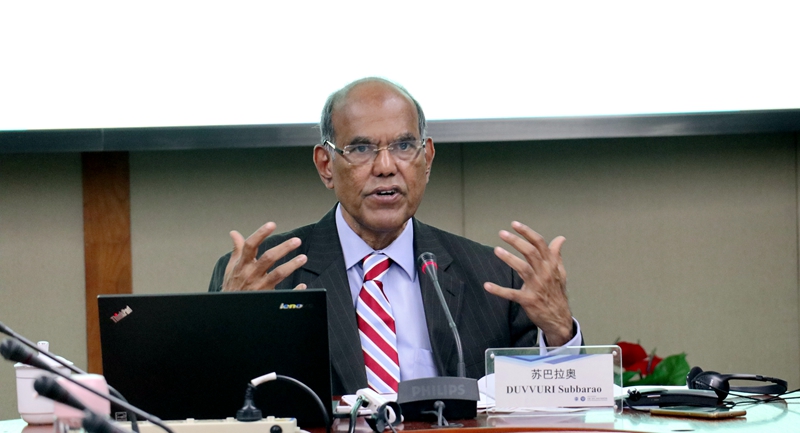
DUVVURI Subba Rao, Former Governor of the Reserve Bank of India and Distinguished Visiting Fellow, National University of Singapore
15:35-16:25 Q&A
16:25-16:30 Closing Remarks
Highlights
Dr. Duvvuri Subba Rao served as Governor of the Reserve Bank of India for five years (2008-13). Prior to that, he was Finance Secretary to the Government of India from 2007-08 and Secretary to the Prime Minister’s Economic Advisory Council 2005-07. He is currently a Distinguished Visiting Fellow at the National University of Singapore.
Dr. Subba Rao came in as Governor of the Reserve Bank of India just a week before the global financial crisis erupted in full in mid-September 2008 and he led the effort to mitigate the impact of the crisis on the Indian economy and to institute economic and financial sector reforms reflecting the lessons of the crisis.
- I. Enhance Mutual Trust among the BRICS
Nowadays, with rapid development of BRICS cooperation, its global influence is increasingly enlarged, stimulating profound adjustment of world structure. However, with the raging anti-globalization thoughts and the intensifying trade frictions, how can the BRICS better express “BRICS voice” as a whole?
The BRICS should take a united stance to cope with the intensifying trade disputes. At present, under the background of continuous trade frictions, the BRICS should, on one hand, manage and control divergence, strengthen the coordination and cooperation in economic and trade, and on the other hand, fully utilize the New Development Bank of the BRICS, the BRICS Contingent Reserve Arrangement and other cooperation mechanisms with the aim of improving the collective risk resistance capacity of the BRICS and relieve the trading relationship.
The BRICS ought to take advantage of respective strength while deepening the coordination and development of BRICS during industrialization. At the moment, as the BRICS are all in their key period of economic structural transformation, upgrading and development, they shall speed up the industrialization of the BRICS by continuing to enhance their cooperation in industries, including production capacity and industrial policy, new industrial infrastructure construction etc. and give play to the comparative advantages of market resources, production technologies, labor cost and other aspects of each country.
The BRICS are supposed to collectively maintain multilateralism and the multilateral trading system with the core of WTO. Confronting the constant impediment to the development of global free trade, the BRICS shall devote to promoting the reform of WTO and facilitating developing and least developed countries to integrate into multilateral trading system so as to formulate fairer and more transparent international economic and trading rules.
- II. Boost Sino-Indian Cooperation
China and India, with huge domestic markets and distinguished resources, are strong in economic mutual complements and enormous in cooperation potential. Therefore, boosting Sino-Indian practical cooperation will not only help to elevate the position of developing countries in global value chain, but also greatly affect the stability of regions around China and India.
Based on the mutual complement of industrial structure of the two countries, it is possible for China and India to deepen the cooperation in processing and manufacturing, infrastructure construction, information technology and pharmacy and other fields. In consideration of the different development process of industrialization of China and India, the two countries shall make use of comparative advantages in an attempt to coordinate the avocation of “The Belt and Road” and the plan of “Make in India”, and meanwhile, expedite the integration of more emerging markets and developing countries into the global industrial division system.
It is necessary for China and India to facilitate Sino-Indian trade and investment by enhancing financial cooperation. The cooperation between the two sides on banks and other financial organizations shall be strengthened and the investment, financing and credit system shall be optimized, in order to provide convenient payment, settlement, financing and other services for the investment and trade between two countries’ enterprises, and ultimately broaden and deepen the mutual economic and trade cooperation.
It is a necessity for China and India to strengthen mutual strategic trust and jointly maintain regional stability. The two countries are supposed to communicate and negotiate upon subjects such as the interconnection and interworking construction, the cross-border flow of goods and investment of surrounding regions, so that respective interest can be balanced, providing favorable conditions to realize regional peace and stability, and trade facilitation.
Gallery
https://en.cdi.org.cn/component/k2/item/444-china-india-cooperation-under-brics-framework#sigProId53153643f1