Impact of the COVID-19 epidemic on china’s economy and industrial response

Author: Cao Zhongxiong, Executive Director of New Economy Research Department of CDI
Editor’s note: The impact of this epidemic on the economy can be felt in both short and long terms. In the short term, the economy will be hit hard. In the long run, the epidemic will definitely have a profound impact on China’s industries.
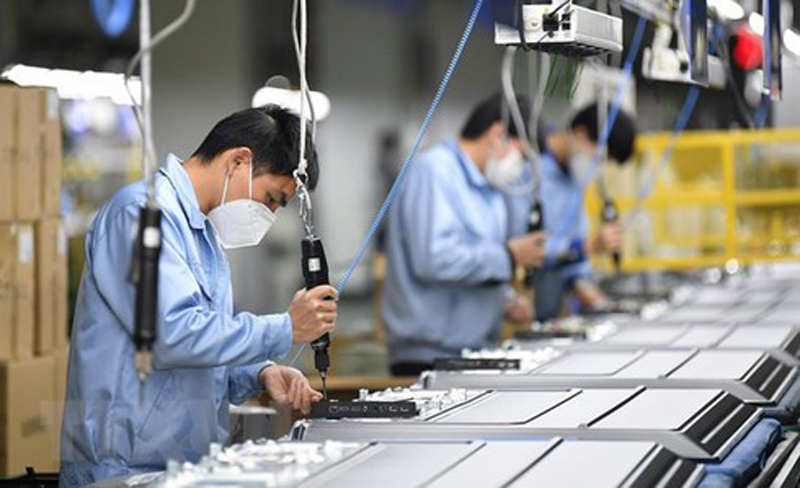
In the short term, consumption, infrastructure and labor-intensive industries will suffer a greater blow. The impact on retail businesses such as shopping centers, wholesale markets and hotels is disastrous. Infrastructure construction, real estate development, and labor-intensive industries, such as textile and clothing among other traditional industries, have been hit hard. Many industries have been temporarily shut down. When it comes to high-tech industries, PCB circuit board manufacturers and mobile phone assembly plants, among other labor-intensive enterprises in the field of electronic information, are greatly affected.
Moreover, it is also a hard time for small and medium-sized start-ups, which are less resilient against risks. Declining sales, rising labor costs and high uncertainties have exacerbated difficulties in their operation. If one enterprise has an epidemic situation, its staff will be quarantined and production halted, which means it will be practically out of business. In particular, start-ups are burdened by rent and wages in an overall hostile financing environment. Many start-ups, which are not able to profit, face mounting pressure of survival in this time of extraordinary hardship.
It is important that the government readjust its economic policy, industrial policy and tax policy as soon as possible and make policy arrangements during the epidemic. While controlling the epidemic, the government shall also introduce new economic control policies, such as increasing tax relief, lowering or deferring social insurance payments, and providing subsidies for key industries, so as to ease the difficulties of enterprises. It is also important that enterprises adjust their production plans and formulate work-from-home measures as soon as possible to minimize adverse effects, and be ready to resume production after the epidemic is over and make up for production delayed by the epidemic.
In the long run, the epidemic will definitely have a profound impact on China’s industries. The health industry has always been a key area for consumption upgrading. After this epidemic, the public awareness of health will be further enhanced. Health protection, medical care and sports will embrace further opportunities of development. People’s health awareness will extend from the demand for masks to other fields.
During this epidemic, e-commerce and Internet companies have played a role in epidemic prevention while providing convenience for people’s daily life. Life-related e-commerce companies have served as a channel for providing daily necessities for people staying at home. In the future, with the development of 5G infrastructure, Internet-related industries will once again usher in a golden period of development. The reorganization of the Internet no longer means simply more economy of scale, but a further reconstruction of non-Internet fields, a deep integration with hardware and the incorporation of hardware into services.
In first-tier and second-tier cities, to cope with labor shortage and ensure production during the epidemic, enterprises will use more machines to replace people, as a number of unmanned factories and workshops continue to emerge. Intelligent manufacturing will further strengthen China’s “world factory” status.
Global enterprises, especially multinationals, will further examine their dependence on China’s supply chain, with industrial transfer occurring in certain industries. As multinationals represent a large proportion in China’s manufacturing sector, the epidemic, coupled with Sino-U.S. trade frictions, will compel multinational manufacturers to add new considerations into their plan to optimize their global presence.